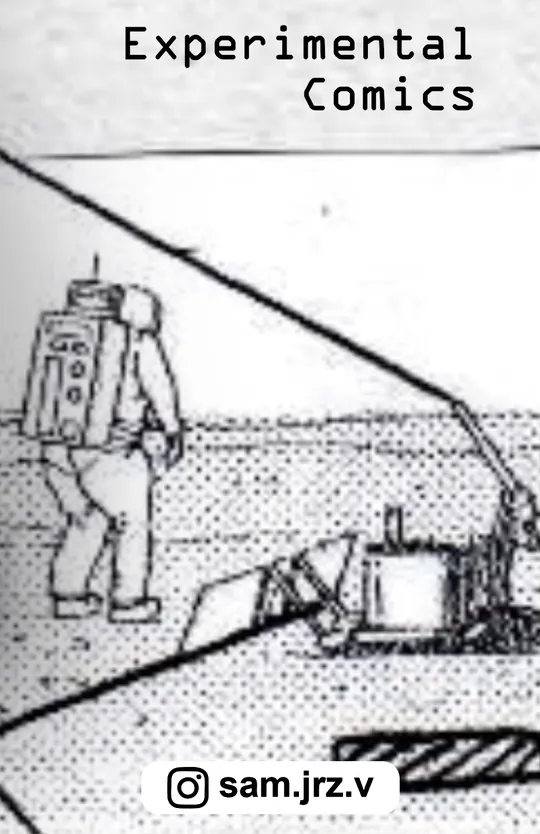
Episode 1
Smart computers
A smart machine is an intelligent device that uses machine-to-machine (M2M) technology.
Smart machines include robots, self-driving cars and other cognitive computing systems that are able to make decisions and solve problems without human intervention
Episode 2
Software
Software is a set of instructions, data or programs used to operate computers and execute specific tasks. It is the opposite of hardware.
Episode 3
Hardware
Computer hardware is a collective term used to describe any of the physical components of an analog or digital computer.
Episode 4
Think
In their most common sense, the terms thought and thinking refer to cognitive processes that can happen independently of sensory stimulation. Their most paradigmatic forms are judging, reasoning, concept formation, problem solving, and deliberation. But other mental processes, like considering an idea, memory, or imagination, are also often included.
Episode 5
Rationality
Rationality is the quality of being guided by or based on reason. In this regard, a person acts rationally if they have a good reason for what they do, or a belief is rational if it is based on strong evidence.
Episode 6
Action
In philosophy, an action is an event that an agent performs for a purpose, that is, guided by the person's intention.
Episode 7
Agent
In the United States, a special agent is an official title used to refer to certain investigators or detectives of federal, military, tribal, or state agencies who primarily serve in criminal investigatory positions.
Episode 8
Test
A procedure intended to establish the quality, performance, or reliability of something, especially before it is taken into widespread use
Episode 9
Language
The principal method of human communication, consisting of words used in a structured and conventional way and conveyed by speech, writing, or gesture.
Episode 10
Knowledge
Knowledge is an awareness of facts, a familiarity with individuals and situations, or a practical skill. Knowledge of facts, also called propositional knowledge, is often characterized as true belief that is distinct from opinion or guesswork by virtue of justification. While there is wide agreement among philosophers that propositional knowledge is a form of true belief, many controversies focus on justification.

 English
English